Service Center
Definition and scope
Service Centers are in charge of the delivery of services to one or several customers.
Service Centers may be hosted on customer premises or at the service provider’s offices (remote service providing).
Service Centers are steered by the service provider.
These added-value services are carried out from start to end and they are industrialized and measurable.
Setting up a service center allows the following:
- Improve the way customers and subcontractors work together
- Reach a better efficiency by sharing good practices in any given project
- An actual economy of scale by pooling available resources
- Acquiring and keeping up high levels of competence and implementing state-of-the-art technologies
- Ensuring service continuity

Definition of services
In-service Support :
Incident management – production follow-up
User assistance
Corrective/evolutive maintenance
Project realization
Project implementation
Test (reception, acceptance)
Service scoping documentation
Service providing contract
It defines the commitments of both parties
Service agreement
It defines the services and how they’re measured
Guaranteed quality agreement (GQA)
It describes both the organization and the process of the CELAD Service Center. It standardizes exchanges between the customer and the Service Center
Requests formalization
Mission requirement is formalized by the customer through a service request
Objective : formalizing and following up on the customer’s request
- Service request formalization by the customer
- Service Center proposal formalization by CELAD
- Validation of the Service Center proposal by the customer
Request contractualization
Fixed-price commitment:
- Writing of an Estimate
- Based either on work-package estimation method or on “expert’s statement”
- Estimate approval by the customer
- Writing of a fixed-price service contract
Technical Assistance :
- Proposal
- Approval of said proposal by the customer
- Writing of a purchase order
Macro Steering
Steering committee (Customer/Service Center)
Frequency: monthly
Goals: overall service desk activity follow-up, arbitrage and decisions.
Operational committee (Customer/Service Center)
Frequency: weekly
Goals : detailed operational activity follow-up, tasks coordination, checkpoint on commitments.
Quality committee (Customer/Service Center)
Frequency: quarterly
Goals: overall service follow-up and quality control
Micro Steering
Mission follow-up committee (Customer/Service Center)
Frequency: weekly
Goals: Mission follow-up regarding workload, deadlines, actions follow-up, risk management
Internal follow-up committee (Service Center)
Frequency: weekly
Goals: Mission internal follow-up regarding workload, deadlines, actions follow-up, risk management
Mission quality plan (Customer/Service Center)
For applications covered by in-service support or projects>100 days.
In addition to the GQA regarding missions specificities.
5-phase life cycle
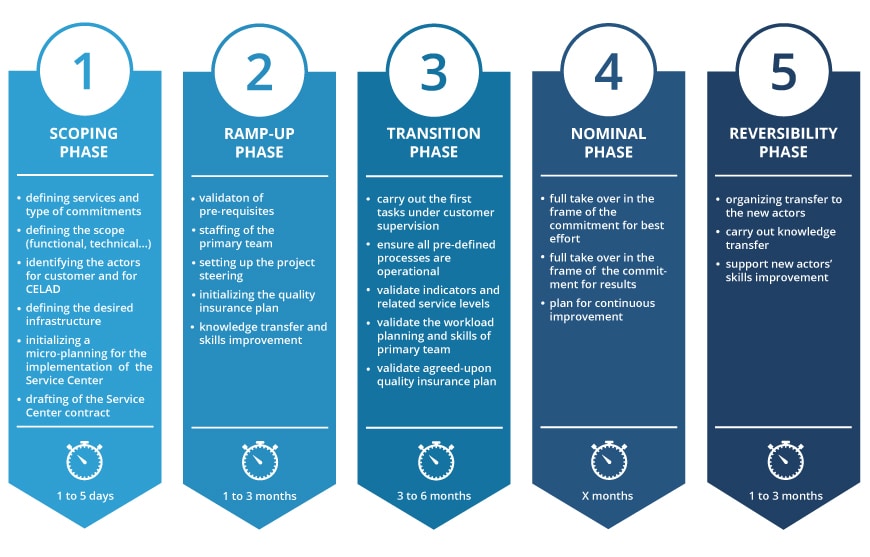
Customer responsibility
Scoping
phase
Identification of the Service Center steering responsible.
Definition of service
Definition of scope (technical, functional…)
Initialization
phase
GQA approval
Approval of indicators and expected service levels
Partaking in the know-transfer and workload build-up phases
Operational
phase
Partaking in various committees
Writing and validation of service requests
Validation of purchase orders and fixed-price contracts
Writing of requirement statements, technical specifications…
Acceptance of deliverables.
Our references

Banking sector
- 150 collaborators
- 63 applications
- Large systems, PACBASE, DB2, DL1.
- Scalable maintenance.

In the field of connected objects/wearables
- Design, development/integration, validation and support for connected objects such as connected watches/glasses/wristbands
- Kinux kernel, C, Androidwear, Python, mobility (iOS/Android)
- Expertise in the following fields: baseport, connectivity (Wifi, Bluetooth, BLE, GPS, NFC…), audio, bootloader/Flashing, Firmware Over The Air, Power & Energy management, Dev apps iOS/Android
- 140 collaborators
